On this article, you’ll learn to flip free-form massive language mannequin (LLM) textual content into dependable, schema-validated Python objects with Pydantic.
Matters we’ll cowl embody:
- Designing sturdy Pydantic fashions (together with customized validators and nested schemas).
- Parsing “messy” LLM outputs safely and surfacing exact validation errors.
- Integrating validation with OpenAI, LangChain, and LlamaIndex plus retry methods.
Let’s break it down.
The Full Information to Utilizing Pydantic for Validating LLM Outputs
Picture by Editor
Introduction
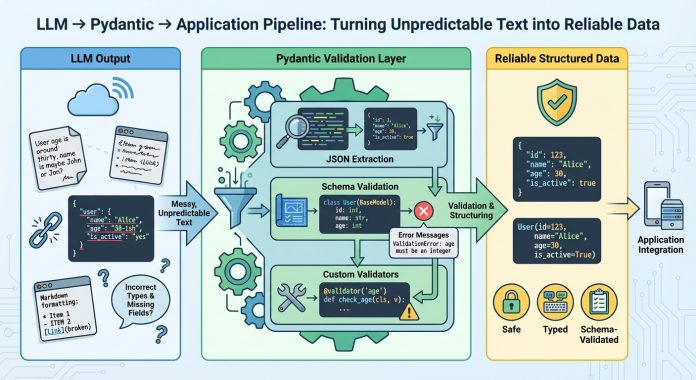
Giant language fashions generate textual content, not structured information. Even if you immediate them to return structured information, they’re nonetheless producing textual content that appears to be like like legitimate JSON. The output could have incorrect area names, lacking required fields, improper information varieties, or further textual content wrapped across the precise information. With out validation, these inconsistencies trigger runtime errors which might be troublesome to debug.
Pydantic helps you validate information at runtime utilizing Python sort hints. It checks that LLM outputs match your anticipated schema, converts varieties routinely the place doable, and gives clear error messages when validation fails. This provides you a dependable contract between the LLM’s output and your utility’s necessities.
This text reveals you methods to use Pydantic to validate LLM outputs. You’ll learn to outline validation schemas, deal with malformed responses, work with nested information, combine with LLM APIs, implement retry logic with validation suggestions, and extra. Let’s not waste any extra time.
🔗 You will discover the code on GitHub. Earlier than you go forward, set up Pydantic model 2.x with the optionally available electronic mail dependencies:
pip set up pydantic[email].
Getting Began
Let’s begin with a easy instance by constructing a device that extracts contact info from textual content. The LLM reads unstructured textual content and returns structured information that we validate with Pydantic:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
from pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStr, field_validator from typing import Elective
class ContactInfo(BaseModel): title: str electronic mail: EmailStr telephone: Elective[str] = None firm: Elective[str] = None
@field_validator(‘telephone’) @classmethod def validate_phone(cls, v): if v is None: return v cleaned = ”.be part of(filter(str.isdigit, v)) if len(cleaned) 10: elevate ValueError(‘Cellphone quantity should have at the very least 10 digits’) return cleaned |
All Pydantic fashions inherit from BaseModel, which gives automated validation. Sort hints like title: str assist Pydantic validate varieties at runtime. The EmailStr sort validates electronic mail format without having a customized regex. Fields marked with Elective[str] = None will be lacking or null. The @field_validator decorator enables you to add customized validation logic, like cleansing telephone numbers and checking their size.
Right here’s methods to use the mannequin to validate pattern LLM output:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
import json
llm_response = ”‘ { “title”: “Sarah Johnson”, “electronic mail”: “sarah.johnson@techcorp.com”, “telephone”: “(555) 123-4567”, “firm”: “TechCorp Industries” } ‘”
information = json.masses(llm_response) contact = ContactInfo(**information)
print(contact.title) print(contact.electronic mail) print(contact.model_dump()) |
While you create a ContactInfo occasion, Pydantic validates the whole lot routinely. If validation fails, you get a transparent error message telling you precisely what went improper.
Parsing and Validating LLM Outputs
LLMs don’t at all times return excellent JSON. Typically they add markdown formatting, explanatory textual content, or mess up the construction. Right here’s methods to deal with these circumstances:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError, field_validator import json import re
class ProductReview(BaseModel): product_name: str ranking: int review_text: str would_recommend: bool
@field_validator(‘ranking’) @classmethod def validate_rating(cls, v): if not 1 v 5: elevate ValueError(‘Ranking have to be an integer between 1 and 5’) return v
def extract_json_from_llm_response(response: str) -> dict: “”“Extract JSON from LLM response which may comprise further textual content.”“” json_match = re.search(r‘{.*}’, response, re.DOTALL) if json_match: return json.masses(json_match.group()) elevate ValueError(“No JSON present in response”)
def parse_review(llm_output: str) -> ProductReview: “”“Safely parse and validate LLM output.”“” strive: information = extract_json_from_llm_response(llm_output) evaluation = ProductReview(**information) return evaluation besides json.JSONDecodeError as e: print(f“JSON parsing error: {e}”) elevate besides ValidationError as e: print(f“Validation error: {e}”) elevate besides Exception as e: print(f“Surprising error: {e}”) elevate |
This strategy makes use of regex to search out JSON inside response textual content, dealing with circumstances the place the LLM provides explanatory textual content earlier than or after the information. We catch totally different exception varieties individually:
JSONDecodeErrorfor malformed JSON,ValidationErrorfor information that doesn’t match the schema, and- Normal exceptions for sudden points.
The extract_json_from_llm_response perform handles textual content cleanup whereas parse_review handles validation, holding considerations separated. In manufacturing, you’d wish to log these errors or retry the LLM name with an improved immediate.
This instance reveals an LLM response with further textual content that our parser handles appropriately:
|
messy_response = ”‘ Right here’s the evaluation in JSON format:
{ “product_name”: “Wi-fi Headphones X100”, “ranking”: 4, “review_text”: “Nice sound high quality, snug for lengthy use.”, “would_recommend”: true }
Hope this helps! ”‘
evaluation = parse_review(messy_response) print(f“Product: {evaluation.product_name}”) print(f“Ranking: {evaluation.ranking}/5”) |
The parser extracts the JSON block from the encircling textual content and validates it towards the ProductReview schema.
Working with Nested Fashions
Actual-world information isn’t flat. Right here’s methods to deal with nested buildings like a product with a number of evaluations and specs:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
from pydantic import BaseModel, Discipline, field_validator from typing import Checklist
class Specification(BaseModel): key: str worth: str
class Overview(BaseModel): reviewer_name: str ranking: int = Discipline(..., ge=1, le=5) remark: str verified_purchase: bool = False
class Product(BaseModel): id: str title: str worth: float = Discipline(..., gt=0) class: str specs: Checklist[Specification] evaluations: Checklist[Review] average_rating: float = Discipline(..., ge=1, le=5)
@field_validator(‘average_rating’) @classmethod def check_average_matches_reviews(cls, v, data): evaluations = data.information.get(‘evaluations’, []) if evaluations: calculated_avg = sum(r.ranking for r in evaluations) / len(evaluations) if abs(calculated_avg – v) > 0.1: elevate ValueError( f‘Common ranking {v} doesn’t match calculated common {calculated_avg:.2f}’ ) return v |
The Product mannequin accommodates lists of Specification and Overview objects, and every nested mannequin is validated independently. Utilizing Discipline(..., ge=1, le=5) provides constraints immediately within the sort trace, the place ge means “larger than or equal” and gt means “larger than”.
The check_average_matches_reviews validator accesses different fields utilizing data.information, permitting you to validate relationships between fields. While you go nested dictionaries to Product(**information), Pydantic routinely creates the nested Specification and Overview objects.
This construction ensures information integrity at each degree. If a single evaluation is malformed, you’ll know precisely which one and why.
This instance reveals how nested validation works with an entire product construction:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
llm_response = { “id”: “PROD-2024-001”, “title”: “Good Espresso Maker”, “worth”: 129.99, “class”: “Kitchen Home equipment”, “specs”: [ {“key”: “Capacity”, “value”: “12 cups”}, {“key”: “Power”, “value”: “1000W”}, {“key”: “Color”, “value”: “Stainless Steel”} ], “evaluations”: [ { “reviewer_name”: “Alex M.”, “rating”: 5, “comment”: “Makes excellent coffee every time!”, “verified_purchase”: True }, { “reviewer_name”: “Jordan P.”, “rating”: 4, “comment”: “Good but a bit noisy”, “verified_purchase”: True } ], “average_rating”: 4.5 }
product = Product(**llm_response) print(f“{product.title}: ${product.worth}”) print(f“Common Ranking: {product.average_rating}”) print(f“Variety of evaluations: {len(product.evaluations)}”) |
Pydantic validates the whole nested construction in a single name, checking that specs and evaluations are correctly fashioned and that the common ranking matches the person evaluation rankings.
Utilizing Pydantic with LLM APIs and Frameworks
Up to now, we’ve discovered that we’d like a dependable strategy to convert free-form textual content into structured, validated information. Now let’s see methods to use Pydantic validation with OpenAI’s API, in addition to frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex. You should definitely set up the required SDKs.
Utilizing Pydantic with OpenAI API
Right here’s methods to extract structured information from unstructured textual content utilizing OpenAI’s API with Pydantic validation:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 |
from openai import OpenAI from pydantic import BaseModel from typing import Checklist import os
shopper = OpenAI(api_key=os.getenv(“OPENAI_API_KEY”))
class BookSummary(BaseModel): title: str writer: str style: str key_themes: Checklist[str] main_characters: Checklist[str] brief_summary: str recommended_for: Checklist[str]
def extract_book_info(textual content: str) -> BookSummary: “”“Extract structured e book info from unstructured textual content.”“”
immediate = f“”“ Extract e book info from the next textual content and return it as JSON.
Required format: {{ “title“: “e book title“, “writer“: “writer title“, “style“: “style“, “key_themes“: [“theme1“, “theme2“], “principal_characters“: [“character1“, “character2“], “transient_abstract“: “abstract in 2–3 sentences“, “really useful_for“: [“audience1“, “audience2“] }}
Textual content: {textual content}
Return ONLY the JSON, no further textual content. ““”
response = shopper.chat.completions.create( mannequin=“gpt-4o-mini”, messages=[ {“role”: “system”, “content”: “You are a helpful assistant that extracts structured data.”}, {“role”: “user”, “content”: prompt} ], temperature=0 )
llm_output = response.selections[0].message.content material
import json information = json.masses(llm_output) return BookSummary(**information) |
The immediate contains the precise JSON construction we anticipate, guiding the LLM to return information matching our Pydantic mannequin. Setting temperature=0 makes the LLM extra deterministic and fewer inventive, which is what we wish for structured information extraction. The system message primes the mannequin to be a knowledge extractor relatively than a conversational assistant. Even with cautious prompting, we nonetheless validate with Pydantic since you ought to by no means belief LLM output with out verification.
This instance extracts structured info from a e book description:
|
book_text = “”“ ‘The Midnight Library’ by Matt Haig is a recent fiction novel that explores themes of remorse, psychological well being, and the infinite prospects of life. The story follows Nora Seed, a lady who finds herself in a library between life and dying, the place every e book represents a unique life she might have lived. By means of her journey, she encounters varied variations of herself and should determine what actually makes a life price dwelling. The e book resonates with readers coping with melancholy, anxiousness, or life transitions. ““”
strive: book_info = extract_book_info(book_text) print(f“Title: {book_info.title}”) print(f“Writer: {book_info.writer}”) print(f“Themes: {‘, ‘.be part of(book_info.key_themes)}”) besides Exception as e: print(f“Error extracting e book data: {e}”) |
The perform sends the unstructured textual content to the LLM with clear formatting directions, then validates the response towards the BookSummary schema.
Utilizing LangChain with Pydantic
LangChain gives built-in help for structured output extraction with Pydantic fashions. There are two principal approaches that deal with the complexity of immediate engineering and parsing for you.
The primary methodology makes use of PydanticOutputParser, which works with any LLM through the use of immediate engineering to information the mannequin’s output format. The parser routinely generates detailed format directions out of your Pydantic mannequin:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate from pydantic import BaseModel, Discipline from typing import Checklist, Elective
class Restaurant(BaseModel): “”“Details about a restaurant.”“” title: str = Discipline(description=“The title of the restaurant”) delicacies: str = Discipline(description=“Sort of delicacies served”) price_range: str = Discipline(description=“Value vary: $, $$, $$$, or $$$$”) ranking: Elective[float] = Discipline(default=None, description=“Ranking out of 5.0”) specialties: Checklist[str] = Discipline(description=“Signature dishes or specialties”)
def extract_restaurant_with_parser(textual content: str) -> Restaurant: “”“Extract restaurant data utilizing LangChain’s PydanticOutputParser.”“”
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Restaurant)
immediate = PromptTemplate( template=“Extract restaurant info from the next textual content.n{format_instructions}n{textual content}n”, input_variables=[“text”], partial_variables={“format_instructions”: parser.get_format_instructions()} )
llm = ChatOpenAI(mannequin=“gpt-4o-mini”, temperature=0)
chain = immediate | llm | parser
outcome = chain.invoke({“textual content”: textual content}) return outcome |
The PydanticOutputParser routinely generates format directions out of your Pydantic mannequin, together with area descriptions and sort info. It really works with any LLM that may comply with directions and doesn’t require perform calling help. The chain syntax makes it straightforward to compose complicated workflows.
The second methodology is to make use of the native perform calling capabilities of recent LLMs via the with_structured_output() perform:
|
def extract_restaurant_structured(textual content: str) -> Restaurant: “”“Extract restaurant data utilizing with_structured_output.”“”
llm = ChatOpenAI(mannequin=“gpt-4o-mini”, temperature=0)
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(Restaurant)
immediate = PromptTemplate.from_template( “Extract restaurant info from the next textual content:nn{textual content}” )
chain = immediate | structured_llm outcome = chain.invoke({“textual content”: textual content}) return outcome |
This methodology produces cleaner, extra concise code and makes use of the mannequin’s native perform calling capabilities for extra dependable extraction. You don’t have to manually create parsers or format directions, and it’s usually extra correct than prompt-based approaches.
Right here’s an instance of methods to use these capabilities:
|
restaurant_text = “”“ Mama’s Italian Kitchen is a comfy family-owned restaurant serving genuine Italian delicacies. Rated 4.5 stars, it is identified for its do-it-yourself pasta and wood-fired pizzas. Costs are reasonable ($$), and their signature dishes embody lasagna bolognese and tiramisu. ““”
strive: restaurant_info = extract_restaurant_structured(restaurant_text) print(f“Restaurant: {restaurant_info.title}”) print(f“Delicacies: {restaurant_info.delicacies}”) print(f“Specialties: {‘, ‘.be part of(restaurant_info.specialties)}”) besides Exception as e: print(f“Error: {e}”) |
Utilizing LlamaIndex with Pydantic
LlamaIndex gives a number of approaches for structured extraction, with significantly robust integration for document-based workflows. It’s particularly helpful when you must extract structured information from massive doc collections or construct RAG techniques.
Probably the most easy strategy in LlamaIndex is utilizing LLMTextCompletionProgram, which requires minimal boilerplate code:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
from llama_index.core.program import LLMTextCompletionProgram from pydantic import BaseModel, Discipline from typing import Checklist, Elective
class Product(BaseModel): “”“Details about a product.”“” title: str = Discipline(description=“Product title”) model: str = Discipline(description=“Model or producer”) class: str = Discipline(description=“Product class”) worth: float = Discipline(description=“Value in USD”) options: Checklist[str] = Discipline(description=“Key options”) ranking: Elective[float] = Discipline(default=None, description=“Buyer ranking out of 5”)
def extract_product_simple(textual content: str) -> Product: “”“Extract product data utilizing LlamaIndex’s easy strategy.”“”
prompt_template_str = “”“ Extract product info from the next textual content and construction it correctly:
{textual content} ““”
program = LLMTextCompletionProgram.from_defaults( output_cls=Product, prompt_template_str=prompt_template_str, verbose=False )
outcome = program(textual content=textual content) return outcome |
The output_cls parameter routinely handles Pydantic validation. This works with any LLM via immediate engineering and is sweet for fast prototyping and easy extraction duties.
For fashions that help perform calling, you should use FunctionCallingProgram. And if you want specific management over parsing habits, you should use the PydanticOutputParser methodology:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
from llama_index.core.program import LLMTextCompletionProgram from llama_index.core.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
def extract_product_with_parser(textual content: str) -> Product: “”“Extract product data utilizing specific parser.”“”
prompt_template_str = “”“ Extract product info from the next textual content:
{textual content}
{format_instructions} ““”
llm = OpenAI(mannequin=“gpt-4o-mini”, temperature=0)
program = LLMTextCompletionProgram.from_defaults( output_parser=PydanticOutputParser(output_cls=Product), prompt_template_str=prompt_template_str, llm=llm, verbose=False )
outcome = program(textual content=textual content) return outcome |
Right here’s the way you’d extract product info in follow:
|
product_text = “”“ The Sony WH-1000XM5 wi-fi headphones characteristic industry-leading noise cancellation, distinctive sound high quality, and as much as 30 hours of battery life. Priced at $399.99, these premium headphones embody Adaptive Sound Management, multipoint connection, and speak-to-chat expertise. Clients charge them 4.7 out of 5 stars. ““”
strive: product_info = extract_product_with_parser(product_text) print(f“Product: {product_info.title}”) print(f“Model: {product_info.model}”) print(f“Value: ${product_info.worth}”) print(f“Options: {‘, ‘.be part of(product_info.options)}”) besides Exception as e: print(f“Error: {e}”) |
Use specific parsing if you want customized parsing logic, are working with fashions that don’t help perform calling, or are debugging extraction points.
Retrying LLM Calls with Higher Prompts
When the LLM returns invalid information, you possibly can retry with an improved immediate that features the error message from the failed validation try:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError from typing import Elective import json
class EventExtraction(BaseModel): event_name: str date: str location: str attendees: int event_type: str
def extract_with_retry(llm_call_function, max_retries: int = 3) -> Elective[EventExtraction]: “”“Attempt to extract legitimate information, retrying with error suggestions if validation fails.”“”
last_error = None
for try in vary(max_retries): strive: response = llm_call_function(last_error) information = json.masses(response) return EventExtraction(**information)
besides ValidationError as e: last_error = str(e) print(f“Try {try + 1} failed: {last_error}”)
if try == max_retries – 1: print(“Max retries reached, giving up”) return None
besides json.JSONDecodeError: print(f“Try {try + 1}: Invalid JSON”) last_error = “The response was not legitimate JSON. Please return solely legitimate JSON.”
if try == max_retries – 1: return None
return None |
Every retry contains the earlier error message, serving to the LLM perceive what went improper. After max_retries, the perform returns None as a substitute of crashing, permitting the calling code to deal with the failure gracefully. Printing every try’s error makes it straightforward to debug why extraction is failing.
In an actual utility, your llm_call_function would assemble a brand new immediate together with the Pydantic error message, like "Earlier try failed with error: {error}. Please repair and take a look at once more."
This instance reveals the retry sample with a mock LLM perform that progressively improves:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
def mock_llm_call(previous_error: Elective[str] = None) -> str: “”“Simulate an LLM that improves primarily based on error suggestions.”“”
if previous_error is None: return ‘{“event_name”: “Tech Convention 2024”, “date”: “2024-06-15”, “location”: “San Francisco”}’ elif “attendees” in previous_error.decrease(): return ‘{“event_name”: “Tech Convention 2024”, “date”: “2024-06-15”, “location”: “San Francisco”, “attendees”: “about 500”, “event_type”: “Convention”}’ else: return ‘{“event_name”: “Tech Convention 2024”, “date”: “2024-06-15”, “location”: “San Francisco”, “attendees”: 500, “event_type”: “Convention”}’
outcome = extract_with_retry(mock_llm_call)
if outcome: print(f“nSuccess! Extracted occasion: {outcome.event_name}”) print(f“Anticipated attendees: {outcome.attendees}”) else: print(“Didn’t extract legitimate information”) |
The primary try misses the required attendees area, the second try contains it however with the improper sort, and the third try will get the whole lot right. The retry mechanism handles these progressive enhancements.
Conclusion
Pydantic helps you go from unreliable LLM outputs into validated, type-safe information buildings. By combining clear schemas with sturdy error dealing with, you possibly can construct AI-powered functions which might be each highly effective and dependable.
Listed here are the important thing takeaways:
- Outline clear schemas that match your wants
- Validate the whole lot and deal with errors gracefully with retries and fallbacks
- Use sort hints and validators to implement information integrity
- Embrace schemas in your prompts to information the LLM
Begin with easy fashions and add validation as you discover edge circumstances in your LLM outputs. Blissful exploring!