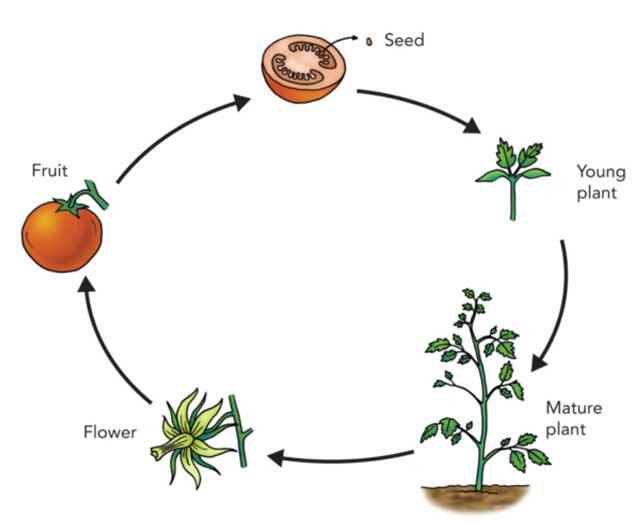
 The lifecycle of vegetation describes how a plant begins its life, grows to maturity, reproduces, and restarts the cycle. Each plant, much like different dwelling issues, follows a particular sequence of phases in its lifecycle that ensures the survival of its species.
The lifecycle of vegetation describes how a plant begins its life, grows to maturity, reproduces, and restarts the cycle. Each plant, much like different dwelling issues, follows a particular sequence of phases in its lifecycle that ensures the survival of its species.
What’s the Plant Life Cycle?
Vegetation are dynamic dwelling organisms that develop and reproduce in a repeating cycle. Their lifecycle begins with a seed and goes by way of varied phases till copy, at which level new seeds are produced and the lifecycle restarts. The lifecycle of vegetation is essential for the survival of vegetation and the upkeep of ecosystems.
Levels of Plant’s Life Cycle
Vegetation start their life journey as seeds. As soon as these seeds are buried within the soil, they germinate. Following germination, they develop first leaves and Roots. From there, vegetation continue to grow till they attain maturity. At this stage, vegetation endure copy by pollination and produce new seeds, restarting the cycle.
In brief, listed below are a very powerful phases that vegetation endure:
- Seed
- Germination
- Seedling
- Rising to Maturity
- Reproductive Stage
- Seed Dispersion
Seed – 1st Stage


Seeds are the embryos of vegetation, full of important vitamins for early progress. These are encased in a tricky outer coating and stay protected till environmental situations turn out to be proper for germination.
These seeds are dispersed naturally throughout the land by way of flowing water, wind, animals, and even human exercise. As soon as a seed reaches an acceptable atmosphere with ample moisture and acceptable Temperature, it germinates and begins its lifecycle.
Germination – 2nd Stage

 When a seed germinates, it awakens from its dormancy and begins to develop. The germination is triggered by moisture, which softens the outer coating and prompts the interior Enzymes. The seed absorbs water and turns into swollen, which breaks the outer coating. The activated enzymes convert the saved vitamins into power that the embryo can use for progress.
When a seed germinates, it awakens from its dormancy and begins to develop. The germination is triggered by moisture, which softens the outer coating and prompts the interior Enzymes. The seed absorbs water and turns into swollen, which breaks the outer coating. The activated enzymes convert the saved vitamins into power that the embryo can use for progress.
Try https://science4fun.data/seed-germination/
Seedling – 3rd Stage


As soon as germination is full, the younger plant emerges from the Soil and is named a seedling. At this stage, the seed has been damaged and the primary roots and leaves of the younger plant are developed.
The primary leaves, often called cotyledons, put together meals for the plant by Photosynthesis. The newly developed roots anchor the plant and take up obligatory vitamins and water from the soil.
Because the seedling develops additional, it grows a plumule. The plumule is the early stem from which new leaves will develop. At this stage, vegetation rely much less on the saved meals and get power from daylight and soil sources.
Rising to Maturity – 4th Stage


After the seedling stage, the plant’s progress and improvement proceed till it reaches full maturity.
Throughout this stage:
- The plant grows quickly and develops many new buildings.
- Its root system deepens and widens for higher assist and nutrient absorption. The stem turns into thicker and elongated to assist its buildings.
- The branches and leaves multiply, which will increase the plant’s means to seize daylight for photosynthesis.
The plant wants many obligatory issues for wholesome progress, corresponding to water, nutrient-rich soil, air, daylight, the proper temperature, and satisfactory spacing from different vegetation. (For particulars, examine How Vegetation Develop?).
As soon as the plant reaches maturity, it strikes to the following vital stage – copy.
Reproductive Stage – 5th Stage
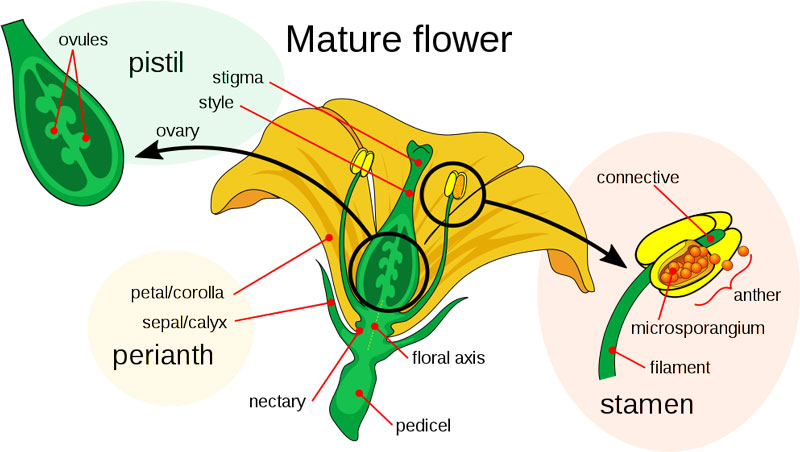
 On this stage, the plant develops flowers for the manufacturing of seeds. It produces flowers from specialised buildings often called determinate Apical Meristem. These are the modified shoot ideas which might be tailored for copy.
On this stage, the plant develops flowers for the manufacturing of seeds. It produces flowers from specialised buildings often called determinate Apical Meristem. These are the modified shoot ideas which might be tailored for copy.
A typical flower consists of each female and male reproductive elements:
- Stamen (Male Half): It produces the pollen (a powdery substance), which incorporates male reproductive cells obligatory for fertilization.
- Pistil (Feminine Half): The pistil is situated on the heart of the flower and incorporates the ovary, which homes the ovules (eggs). When the pollen reaches the pistil, fertilization occurs, and new seeds are produced.
The pollen from male elements reaches to feminine elements by way of wind, bugs, and different pollination strategies.
Seed Dispersion – 6th Stage
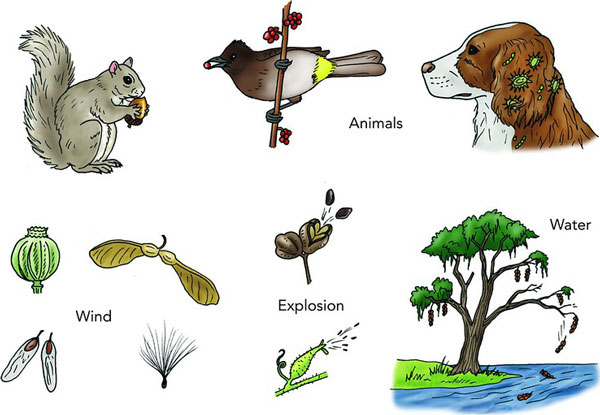
 As soon as seeds are produced, they should attain new favorable places the place they’ll germinate and begin a brand new life cycle. This course of is named seed dispersal, and it’s important for decreasing competitors amongst vegetation of the identical species. Seed dispersal additionally helps vegetation develop in new and far-separated areas.
As soon as seeds are produced, they should attain new favorable places the place they’ll germinate and begin a brand new life cycle. This course of is named seed dispersal, and it’s important for decreasing competitors amongst vegetation of the identical species. Seed dispersal additionally helps vegetation develop in new and far-separated areas.
Strategies for seed dispersion:
- Wind: Robust blows of winds choose the seeds from the vegetation and carry them away. Furthermore, mild seeds with wings or fluffy hairs (e.g., dandelions) glide within the air and attain far locations.
- Water: When seeds of vegetation fall into the river and streams, they’re carried away to distant locations.
- Animals: Fruits of vegetation are eaten by animals that include seeds. Afterward, animals excrete the seeds at totally different places. Additionally, some seeds are sticky and get hooked to animal fur and feathers. They’re carried away by animals and fall off later.
Pollination Strategies
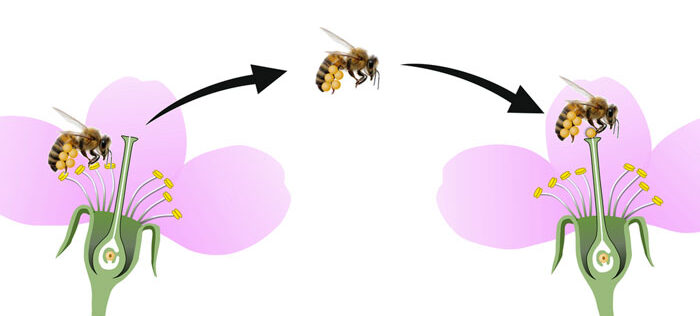

Pollination is the very important course of by which pollen reaches the pistil (feminine half) from the stamen (male half) occurs by way of a number of strategies:
- Insect Pollination: Bugs, corresponding to butterflies, bees, and beetles, are interested in flowers for his or her vibrant colours and candy nectar. These bugs transfer from one flower to a different and unintentionally carry pollen on their our bodies. This manner, the pollen is transferred inside the similar flower and to different flowers.
- Wind Pollination: Many vegetation, corresponding to timber and grasses, rely on wind to hold their light-weight pollen. It’s as a result of these vegetation don’t produce a horny scent or candy nectar. These vegetation produce pollen in giant quantities to extend their probabilities of profitable pollination throughout sturdy winds.
- Animal Pollination: Animals, together with birds and land animals, additionally play a job in pollination, much like bugs. They go to the vegetation for meals and carry the pollen that sticks to their our bodies. They switch pollen from the stamens to the pistils whereas transferring between vegetation and their flower.
What about Seedless Vegetation?


Many vegetation don’t produce flowers or seeds for his or her copy. As a substitute, they develop from the spores of their mum or dad vegetation. Spores are dust-like, tiny reproductive items which might be fashioned by the mum or dad plant. The brand new vegetation develop from these spores when the atmosphere is moist and the temperature is favorable.
See Non-Flowering vegetation for additional info.
FAQs
What’s Self-Pollination and Cross-Pollination?
In self-pollination, the pollen from the anther reaches the stigma in the identical flower, or a distinct flower in the identical plant. Nonetheless, cross-pollination is a bit totally different. It occurs when the pollen from the anther of 1 plant reaches the stigma of one other plant’s flower having the identical species. Each of those processes can occur naturally in addition to artificially.
What’s the Asexual Copy of Vegetation?
The vegetation that develop with out fertilization are referred to as asexually reproduced vegetation. Asexual copy can happen by way of fragmentation, spores, budding, and vegetative propagation. Potatoes are a well-known instance of the asexual copy of vegetation.
What’s the Alternation of Generations?
The life cycle of vegetation is split into two important phases: the haploid and the diploid. These two phases of the plant lifecycle also can alternate, and this course of is named the alternation of generations.
The alternation of generations is the first sort of lifecycle in vegetation. On this lifecycle, the haploid sexual section (gametophytes), which consists of solely a single set of chromosomes, turns right into a diploid asexual section (sporophytes), which incorporates two units of chromosomes. Each haploid and diploid are multicellular, and their cells break up by meiosis and mitosis processes of cell division, respectively. This alternation of era isn’t solely widespread in vegetation but additionally present in algae and Fungi.
Attention-grabbing Details
- The Nice Basin bristlecone pine is the longest-living plant discovered on the earth. Its age is measured to be round 5,056 years.
- Coco de Mer is the seed of a palm tree, it could possibly weigh about 18 Kg (40 kilos) and attain a top of 12 toes.
- Rose, Jasmine, and Lily are the strongest-smelling flowers.
- When a seed isn’t germinating, it’s in a dormant state. On this stage, it’s not more than useless stuff.


