On this article, you’ll be taught sensible prompt-engineering patterns that make massive language fashions helpful and dependable for time collection evaluation and forecasting.
Matters we’ll cowl embody:
- Tips on how to body temporal context and extract helpful alerts
- Tips on how to mix LLM reasoning with classical statistical fashions
- Tips on how to construction information and prompts for forecasting, anomalies, and area constraints
With out additional delay, let’s start.
Immediate Engineering for Time Collection Evaluation
Picture by Editor
Introduction
Unusual as it might sound, massive language fashions (LLMs) will be leveraged for information evaluation duties, together with particular eventualities corresponding to time collection evaluation. The bottom line is to appropriately translate your immediate engineering abilities into the precise evaluation situation.
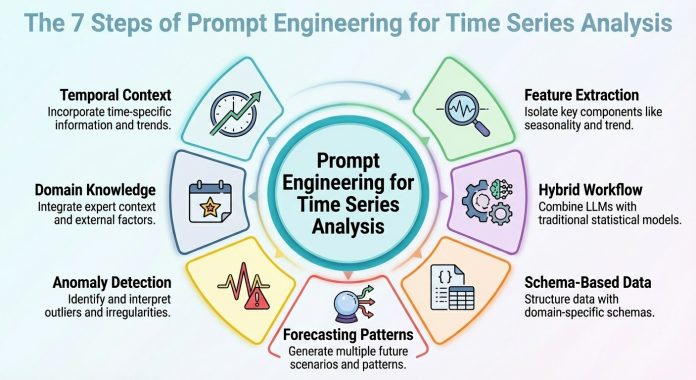
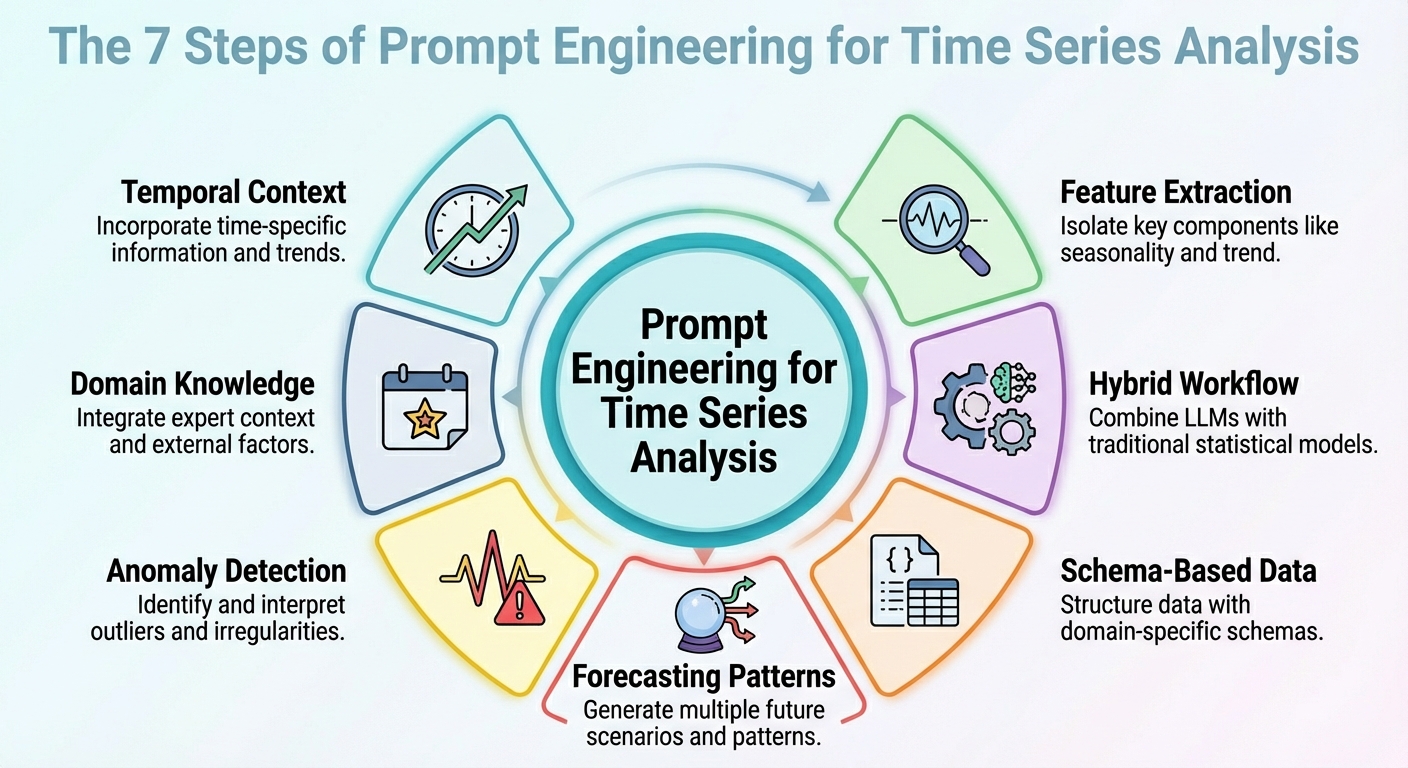
This text outlines seven immediate engineering methods that can be utilized to leverage time collection evaluation duties with LLMs.
Except stated in any other case, the descriptions of those methods are accompanied by illustrative examples revolving round a retail gross sales information situation, concretely, contemplating a time collection dataset consisting of day by day gross sales over time for its evaluation.
1. Contextualizing Temporal Construction
First, an efficient immediate to get a helpful mannequin output must be one which helps it perceive the temporal construction of the time collection dataset. This contains potential mentions of upward/downward tendencies, seasonality, recognized cycles like promotions or holidays, and so forth. This context info will assist your LLM interpret, as an illustration, temporal fluctuations as — properly, simply that: fluctuations, slightly than noise. In sum, describing the construction of the dataset clearly within the context accompanying your prompts usually goes additional than intricate reasoning directions in prompts.
Instance immediate:
“Right here is the day by day gross sales (in items) for the final one year. The information reveals a weekly seasonality (increased gross sales on weekends), a regularly rising long-term pattern, and month-to-month spikes on the finish of every month resulting from pay-day promotions. Use that data when forecasting the following 30 days.”
2. Function and Sign Extraction
As a substitute of asking your mannequin to carry out direct forecasts from uncooked numbers, why not immediate it to extract some key options first? This might embody latent patterns, anomalies, and correlations. Asking the LLM to extract options and alerts and incorporate them into the immediate (e.g., by way of abstract statistics or decomposition) helps reveal the explanations behind future predictions or fluctuations.
Instance immediate:
“From the previous one year of gross sales information, compute the common day by day gross sales, the usual deviation, determine any days the place gross sales exceeded imply plus twice the usual deviation (i.e., potential outliers), and observe any recurring weekly or month-to-month patterns. Then interpret what elements may clarify high-sales days or dips, and flag any uncommon anomalies.”
3. Hybrid LLM + Statistical Workflow
Let’s face it: LLMs in isolation will usually battle with duties requiring numeric precision and capturing temporal dependencies in time collection. Because of this, merely combining their use with classical statistical fashions is a system to yield higher outcomes. How might a hybrid workflow like this be outlined? The trick is to inject LLM reasoning — high-level interpretation, speculation formulation, and context comprehension — alongside quantitative fashions corresponding to ARIMA, ETS, or others.
As an illustration, LeMoLE (LLM-Enhanced Combination of Linear Consultants) is an instance of a hybrid method that enriches linear fashions with prompt-derived options.
The consequence blends contextual reasoning and statistical rigor: the very best of two worlds.
4. Schema-based Information Illustration
Whereas uncooked time collection datasets are normally poorly suited codecs to move as LLM inputs, utilizing structured schemas like JSON or compact tables might be the important thing that enables the LLM to interpret these information way more reliably, as demonstrated in a number of research.
Instance JSON snippet to be handed alongside a immediate:
|
{ “gross sales”: [ {“date”: “2024-12-01”, “units”: 120}, {“date”: “2024-12-02”, “units”: 135}, ..., {“date”: “2025-11-30”, “units”: 210} ], “metadata”: { “frequency”: “day by day”, “seasonality”: [“weekly”, “monthly_end”], “area”: “retail_sales” } } |
Immediate to accompany the JSON information with:
“Given the above JSON information and metadata, analyze the time collection and forecast the following 30 days of gross sales.”
5. Prompted Forecasting Patterns
Designing and correctly structuring forecasting patterns inside the immediate — corresponding to short-term vs. long-term horizons or simulating particular “what-if” eventualities — might help information the mannequin to provide extra usable responses. This method is efficient for producing extremely actionable insights on your requested evaluation.
Instance:
|
Activity A — Brief–time period (subsequent 7 days): Forecast anticipated gross sales.
Activity B — Lengthy–time period (subsequent 30 days): Present a baseline forecast plus two eventualities: – State of affairs 1 (regular situations) – State of affairs 2 (with a deliberate promotion on days 10–15)
In addition, present a 95% confidence interval for each eventualities. |
6. Anomaly Detection Prompts
This one is extra task-specific and focuses on correctly crafting prompts which will assist not solely forecast with LLMs but additionally detect anomalies — together with statistical strategies — and motive about their probably causes, and even recommend what to analyze. The bottom line is, as soon as extra, to first preprocess with conventional time collection instruments after which immediate the mannequin for interpretation of findings.
Instance immediate:
“Utilizing the gross sales information JSON, first flag any day the place gross sales deviate greater than 2× the weekly commonplace deviation from the weekly imply. Then for each flagged day, clarify potential causes (e.g., out-of-stock, promotion, exterior occasions) and suggest whether or not to analyze (e.g., test stock logs, advertising and marketing marketing campaign, retailer foot site visitors).”
7. Area-Infused Reasoning
Area data like retail seasonality patterns, vacation results, and so forth., uncovers priceless insights, and embedding it into prompts helps LLMs carry out analyses and predictions which might be extra significant and likewise interpretable. This boils right down to leveraging the relevance of “dataset context,” each semantically and domain-specific, because the lighthouse that guides mannequin reasoning.
A immediate like this might assist the LLM do higher at anticipating month-end spikes or gross sales drops resulting from vacation reductions:
“That is the day by day gross sales information of a retail chain. Gross sales are likely to spike on the finish of every month (prospects obtain salaries), drop on public holidays, and improve throughout promotional occasions. There may be additionally an occasional inventory scarcity, leading to dips for sure SKUs. Use this area data when analyzing the collection and forecasting.”
Wrapping Up
This text described seven completely different methods, largely based and supported by latest research, to make more practical prompts for time collection evaluation and forecasting duties aided by LLMs.